Understanding Nutritional Needs During Pregnancy: A Focus on Vegetarian Diets.
Over the past few years, the number of vegetarian and vegan diets has grown considerably. Maintaining a suitable environment for the best possible development of the baby throughout pregnancy depends on the mother’s health and, by extension, the health of her kids. Pregnancy brings about changes in the mother’s digestion and body growth, as well as an increase in nutrients.

From development to delivery, the physiological changes that occur during pregnancy are immediate and considerable. To continue the mother’s metabolism and tissue accretion while promoting the growth and development of the baby, maternal nutrition requirements rise.
The Vital Role of Protein in Pregnancy: Why It Matters?
To ensure a healthy, fully developed birth, pregnant women must consume enough calories and protein in their diet as per RDA.
The importance of protein-rich food during pregnancy
- Enhances fetal development
- Reduce the chance of low-birth-weight babies, premature deliveries, and small-for-gestational-age babies.
- Improves the results of birth
Balancing Protein Intake: Risks of Too Little or Too Much During Pregnancy.
Human undernutrition and overnutrition caused by mothers (during pregnancy) are known to result in oxidative stress, high blood cortisol levels, and nutritional imbalances such as excess or deficiency in protein uptake.
Low levels of maternal dietary protein can lead to deficiencies in certain amino acids that are important for cell metabolism and function, which can result in lower newborn growth, restricted growth in the womb, and fetal loss.
An excessive amount of protein or AAs (amino acids) can unfunctional processes, which can lead to poor maternal health, loss of pregnancy, intrauterine growth restriction, and embryonic/fetal death.
How Much Protein Do You Need During Pregnancy? RDA Insights.
| Weight of patient (kg) | WEIGHT of pregnant patient during first trimester (kg) | Total protein requires during the first trimester (g/day) | Weight of patient during the second and third trimester (kg) | Total protein requires during the second and third trimesters (g/day) |
| 30-40 (kg) | 31-41 (kg) | 24-32 (g/day) | 43-53 (kg) | 34-42 (g/day) |
| 45-60 (kg) | 46-61 (kg) | 36-48(g/day) | 58-73 (kg) | 46-58 (g/day) |
| 65-85 (kg) | 66-86 (kg) | 52-68(g/day) | 78-98 (kg) | 62-78 (g/day) |
These estimated average requirements (EAR) correspond to a daily protein consumption of 38 g in the first trimester and 59 g in the second and third trimesters, assuming a standard body weight for women.
Protein for Two: 5 Vegetarian Foods for a Healthy Pregnancy Journey.
1. Chickpeas
Important vitamins including riboflavin, niacin, thiamine, folate, and the precursor to vitamin A, β-carotene, are all found in good amounts (164 grams/day) in chickpeas.
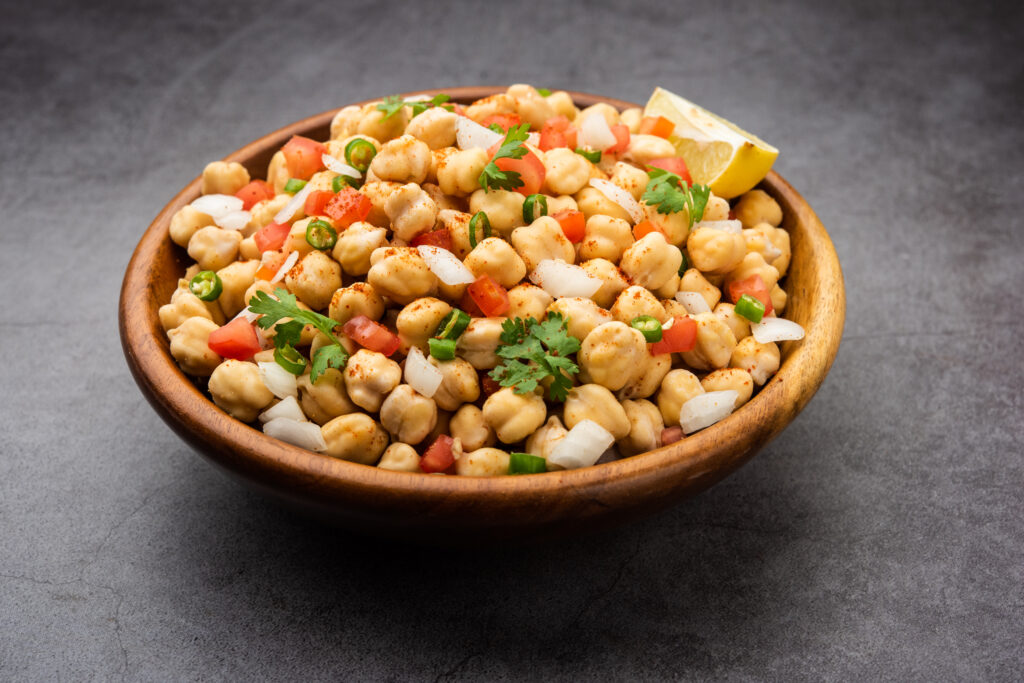

Certain significant human conditions, such as digestive disorders, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain malignancies, may benefit from it.
2. Chia seeds
Research has demonstrated the health benefits of chia seeds, including enhanced blood lipid profiles, low blood pressure and lower blood sugar levels, antioxidant and antibacterial properties, and immuno-stimulatory effects.
3. Walnuts
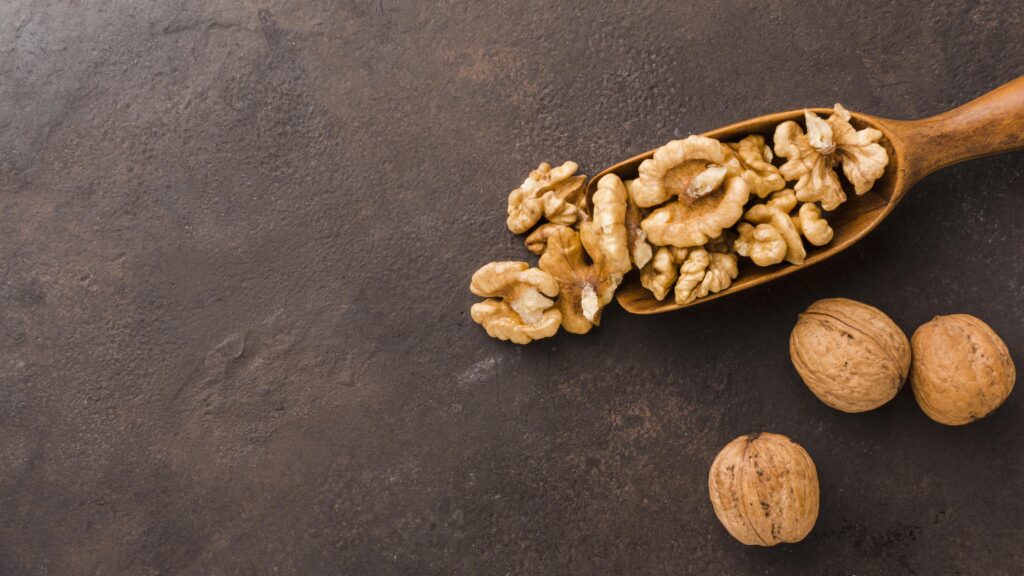

Walnuts are high in antioxidants and heart-healthy lipids. Frequent walnut consumption may help prevent cancer and heart disease as well as increase brain function.
4. Beans
Due to their high protein, fibre content, complex carbohydrate content, folate, zinc, iron, and magnesium content, and low saturated and total fat content, beans may be a good option for improving nutrient intake during pregnancy. Eating beans at least once a week (60 grams) may enhance the quality of a mother’s diet.
5. Cereals
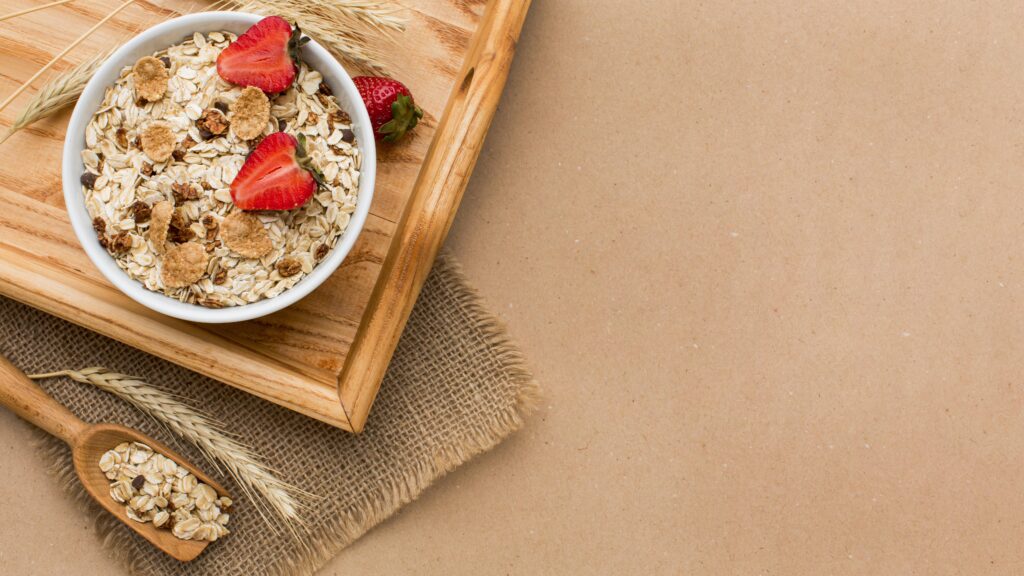

For proper placental and fetal development, cereals are enriched with essential nutrients like folic acid, iron, zinc, calcium, and vitamins A, C, and D.
Nourishing Futures: The Power of Vegetarian Protein During Pregnancy.
Healthy dietary practices throughout pregnancy have a long-lasting beneficial impact on the development and growth of the baby you’re expecting. A vegetarian protein diet is crucial for pregnant women since it enhances maternal health and promotes healthy fetal growth, as the above-mentioned studies demonstrate.