Fasting: A voluntary abstinence/reduction of some or all food, drink, or both (absolute), for a period of time lasting typically between 12 h and 3 weeks to focus on health and/or spiritual uplift. Each and every religion have a long tradition of short ( as short fasting up to 7 days) or prolonged fasting (fasting more than 7 days to 30 days) in one way or another way.

Paryusan Parv
A recent study published in the Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism on effects of Jain fasting (Paryusan Parv of Jain religion for 3-30 days, the age range was 18-86 in both genders) on the body. Jain fast is water-only fast.
Fasting directly induces calorie restriction, which triggers a complex series of intricate events like stress response activation at the cellular level, improved cleaning out damaged cells, in order to regenerate newer, healthier cells, and alteration in hormonal balance. Various studies have found that fasting protects or improves several cardiometabolic risk factors, such as dyslipidemia (an abnormal amount of lipids) and inflammatory cytokines, diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, and hypertension.
Benefits of Intermittent fasting on various organs of the body
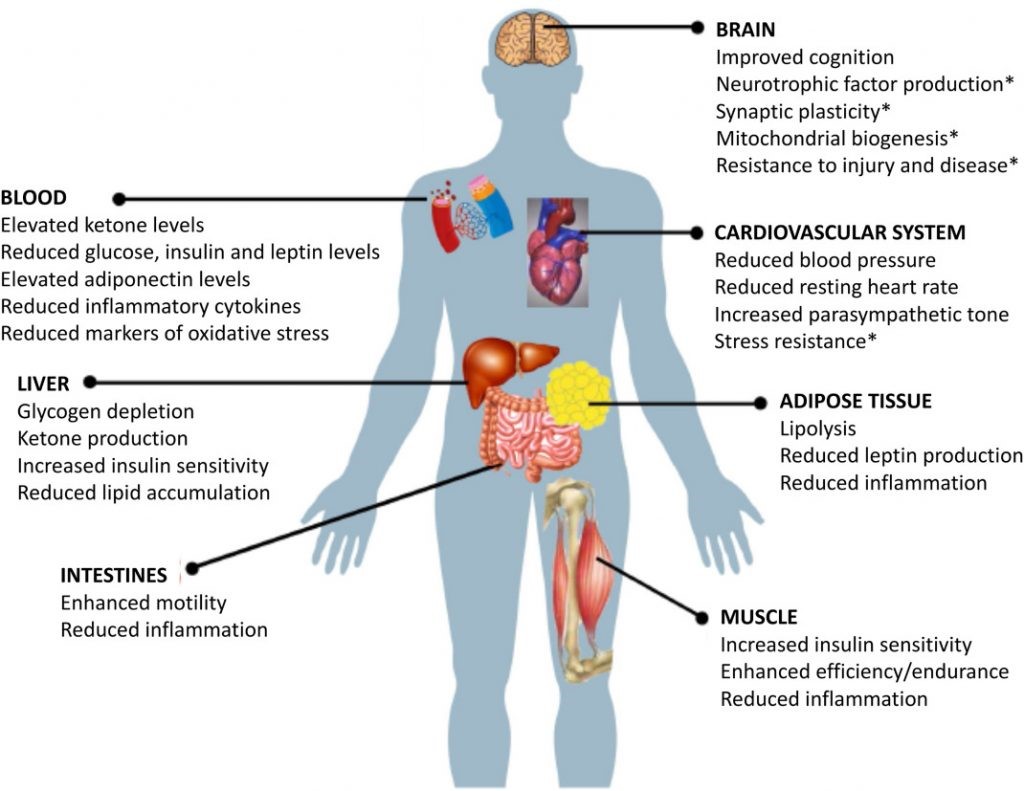
Benefits of intermittent fasting by Dr.Sthephen D Anton et al. Flipping the Metabolic Switch: Understanding and Applying the Health Benefits of Fasting.
Impact of Jain fasting on health i.e. different body parameters was studied like weight, BMI, pulse, blood pressure, lipid profile, renal functions, blood sugar, blood parameters, serum proteins, and serum cortisol, before and after the fast.
The response of the body to Jain fasting
Weight loss: Individuals showed more decrease in weight after Jain fasting, compared to other types of fasting. As in Jain fasting, there is a total cut down of calorie intake and is done solely on water.
BMI: With the notable reduction of weight, the BMI also shows a good reduction. Initially, the reduction in weight and BMI is due to loss of water, loss of body fat, and at a later stage is due to muscle mass reduction.
Lipids: With the reduction in calories, body fat gets mobilized to carbohydrates to fulfill the body’s needs. Triglycerides level increases as a result of this. At the beginning of fast HDL (known as good cholesterol) decreased and LDL (known as bad cholesterol), VLDL, total cholesterol increased, with the progress fast the LDLs, VLDL, and total cholesterol decreased.
Cortisol: Cortisol (an indicator of physical and mental stress) also increased, due to calorie restriction stress on the body.
The study concludes that” Fasting is a cost-effective, non-invasive, has minimal risk of adverse effects for practice in most cases and has the added benefit of improving physical fitness.”
In conclusion, Jain fasting improves BMI, blood pressure, and lipid profile. And serum cortisol is increased during fast.